Title: ISAPP consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics
| Authors: | Salminen et al. |
| Published: | 2021 |
| Journal: | Nature Reviews |

The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) published a consensus statement about the definition and scope of postbiotics.
Postbiotics are referred to as “preparation of inanimate microorganisms and/or their components that confers a health benefit on the target host”.
Please read the full publication here.
ISAPP is a non-profit organization led by a scientific board of directors with input from its industry advisory committee. The like-minded individuals around the world who participate in ISAPP’s activities are committed to advancing the science of probiotics and prebiotics.
Human Milk
Human milk is the best source of nutrition for infants, as it provides a complex and diverse matrix of nutritional and bioactive compounds in an optimal balance of nutrients and other components that are specifically tailored to the infant’s needs.1
The beneficial effects of human milk are due to its many bioactive compounds.2 Of the many compounds of human milk, oligosaccharides, bacteria and their metabolites play a key role in the development of a healthy gut microbiota and immune system.
Infant formula including postbiotics
To harness these potential benefits for the developing infant, infant formula may contain postbiotics. Postbiotics can be produced during fermentation with specific strains of bacteria under carefully controlled conditions. During fermentation bacteria metabolise food and produce various bacterial compounds and metabolites. However, not all postbiotics are the same; strains and fermentation process determine which compounds are being formed, generating unique cells, cell structures, and metabolites with varying functionalities. Therefore the benefits need to be established according to the defined combination of the compounds as these cannot be attributed to any single metabolite alone.
A review article in published in June 2020 Nutrients (Salminen et al) focusses on the current knowledge and future perspective of infant formula supplemented with biotics.
Read more here: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/7/1952/htm
Postbiotics derived during our unique Lactofidus™ fermentation process
One of the postbiotics derived during our Lactofidus™ fermentation process is 3′-galactosyllactose (3′-GL).
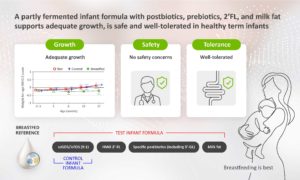
A published article in Nutrients (vandenPlas et al) concluded that a partly fermented infant formula with postbiotics, including 3’ -Galactosyllactose (3’ -GL), prebiotic mixture scGOS/lcFOS (9:1), 2’ -linked fucosyllactose (2’ -FL), and milk fat supports adequate growth, is safe and well-tolerated in healthy term infants. This study was conducted in a double-blind, randomised, controlled, multi-country trial setting.
Read more here: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/11/3560/htm
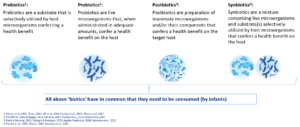
Biotics family
Postbiotics are the most recent addition to the ‘biotics family’ that consists of prebiotics, probiotics and synbiotics.
In 2019, Wiley published an Essential Knowledge Briefing ‘The biotics family in early life’ which examines the role of ‘dietary biotics’ in supporting the development of a healthy, balanced gut microbiota and immune system.
Please click here to read more https://www.danoneresearch.com/essential-knowledge-briefing-the-biotics-family-in-early-life
Find out more about our research into ‘Immunity through Gut’ here: https://www.danoneresearch.com/immunity-through-gut/
References:
1 WHO Growth Standards. http://www.who.int/childgrowth/en/. 2006.
2 Ballard O, Morrow AL. Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr Clin North Am 2013;60:49-74.